
Nodes must join each group individually.The Internet of Things (IoT) approach relies on the use of the Internet Protocol (IP) as a pervasive network protocol. This is shown by an "X" in the scope field of the address thatĪs defined in, IPv6 multicast addresses which are only different Variable Scope Multicast Addresses Registration Procedure(s) Expert Review Reference Note These permanently assigned multicast addresses are valid over all scope Such RFCs are expected to make an explicit request to Registry as an additional reference in the Realm-Local scopeĮntry. Scope definition would be appropriate for publication in anĪny RFCs that define a Realm-Local scope will be listed in this Technology should be published in an RFC.

IPv6 Multicast Address Scopes Registration Procedure(s) IETF Review Reference Note The definition of any Realm-Local scope for a particular network Unicast-based (Including SSM) Multicast Group IDs.IPv6 multicast addresses not listed below are reserved. The rules for assigning new IPv6 multicast addresses are defined in

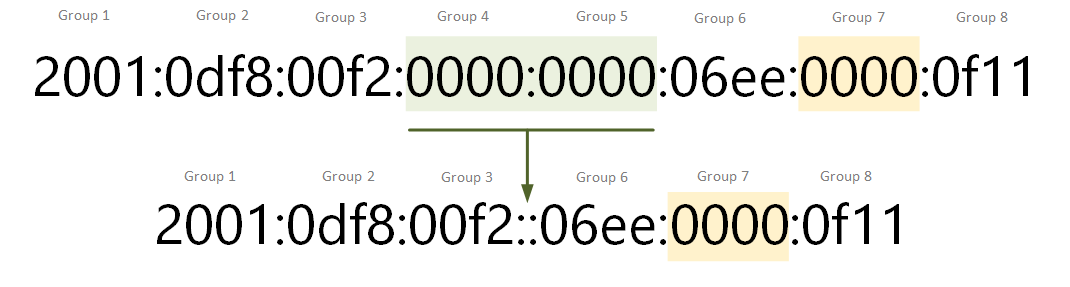
Identifies an address as a unicast address. Value of the high-order octet of the addresses: a value of 0xFF (binaryġ1111111) identifies an address as a multicast address any other value IPv6 multicast addresses are distinguished from unicast addresses by the This defines fixed scope and variable scope
IPv6 Multicast Address Space Registry Last Updated Expert(s) Stig Venaas Note IPv6 multicast addresses are defined in "IP Version 6 AddressingĪrchitecture".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
